IEC Abstract:
IEC 62607-9-1: 2021 establishes a standardized method to characterize spatially varying magnetic fields with a spatial resolution down to 10 nm for flat magnetic specimens by magnetic force microscopy (MFM). MFM primarily detects the stray field component perpendicular to the sample surface. The resolution is achieved by the calibration of the MFM tip using magnetically nanostructured reference materials.
The objective of this IEC Technical Specification is to define and describe:
- reference materials for traceable high resolution magnetic stray field measurements;
- the calibration procedures to determine the instrument calibration function (ICF) and, if required, MFM key parameters entering the deconvolution process;
- the deconvolution process which allows to calculate quantitative stray field data from the measured MFM data using the ICF;
- the evaluation of the measurement uncertainty, including the prevention of potential artefacts which can occur during the measurement leading to a misinterpretation of the results.
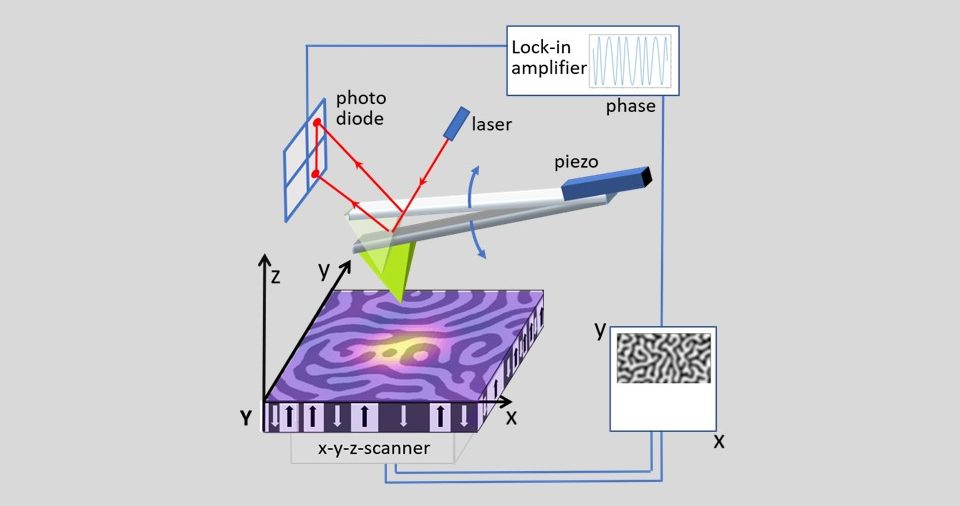
Picture: Cantilever of the magnetic force microscope scanning nanoscale magnetic domains (With permission of Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt)
Buy the standard at the IEC Webstore
 The scientific work to evaluate the measurement and analytic principles have been carried out under the Joint Research Project (JRP) NanoMag and has received funding from the EMPIR programme co-financed by the Participating States and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.
The scientific work to evaluate the measurement and analytic principles have been carried out under the Joint Research Project (JRP) NanoMag and has received funding from the EMPIR programme co-financed by the Participating States and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.